Integrating an Identity Provider
cidaas allows the integration of third-party Identity Providers (IDP). We simply call this entity the "Login Provider" or "Identity Provider". Thereby, a person can use their identity from another system to authenticate or register on cidaas and thus on your applications.
| Advantages | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Convenient Registration | Typically in Consumer / Customer Identity and Access Management it is worth also providing widely used Social Login Providers. Therefore you can enable Single Sign On using the SSO-Feature of the Login Provider, easy registration with social login information and achieve a convenient onboarding. |
| Migration | Integrate the user base of your previous identity provider for user migration, provides an easy migration from the previous system to cidaas. |
| Bring Your Own Identity | In a B2B-Context, your Customers mostly already have their own identity system. Achieving a convenient authentication on your provided services, you can allow your customers to authenticate using their IAM, known as Bring Their Own Identity. |
General Settings
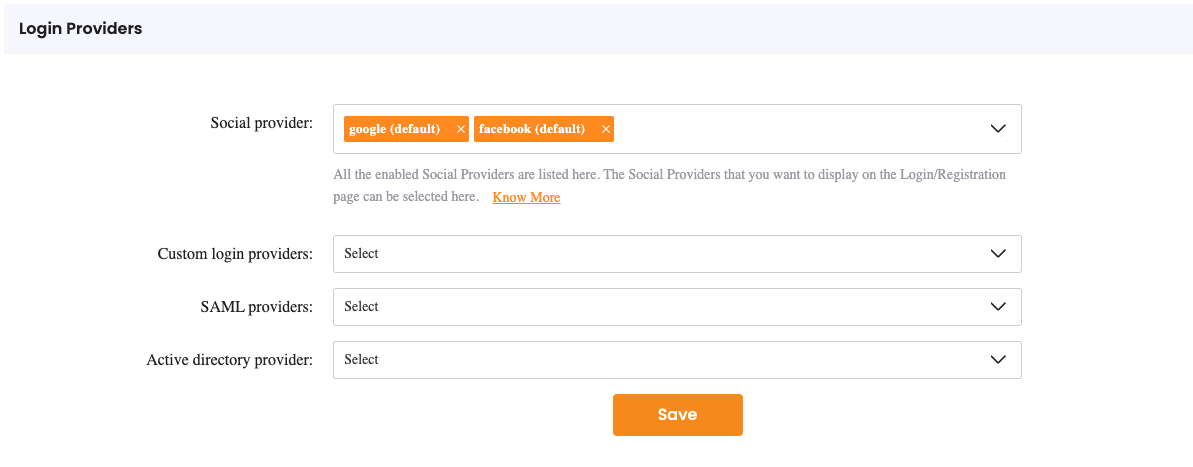
In App Settings you can select which login provider should be shown on the login page, or allowed for the domain-based webfinger
| App Settings | Description |
|---|---|
| Provider | The image below shows the Selection of Providers in your App Settings. |
| Allow Registration with Social Information | Furthermore, you need to allow to register with social information, otherwise, a login will only work for created users beforehand. For information about linking multiple identity providers to a single user account, see Account Linking. |
| Autologin | Enable autologin to automatically authenticate users with their configured identity provider without requiring manual login selection. This works in conjunction with domain-based webfinger to provide seamless authentication experience. |
Provider Types
cidaas supports multiple identity provider standards. Each standard can be used in two ways:
- cidaas as Identity Provider (IdP): cidaas provides user identity to external applications
- cidaas as Service Provider (SP): cidaas receives user identity from external identity providers
SAML 2.0
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an XML-based standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data.
Use Cases:
- Enterprise SSO with SAML-compliant applications
- Federated identity with external SAML identity providers
- B2B identity federation
Documentation:
- SAML Integration - Complete guide for SAML as IDP and SP
OAuth2/OIDC
OAuth2 and OpenID Connect (OIDC) are modern standards for authentication and authorization.
Use Cases:
- Social login (Google, Facebook, etc.)
- Custom OAuth2/OIDC provider integration
- Modern web and mobile application authentication
- API access control
Documentation:
- OAuth2/OIDC Integration - Complete guide for OAuth2/OIDC as IDP and SP
- Social Login Providers - Social provider setup guides
LDAP/Active Directory
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) and Active Directory are directory services for user management and authentication.
Use Cases:
- Enterprise directory integration
- User synchronization from existing directories
- Active Directory SSO
- LDAP-based authentication
Documentation:
- LDAP/Active Directory Integration - Complete guide for LDAP/AD as IDP and SP
Quick Reference
| Standard | cidaas as IDP | cidaas as SP | Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAML | ✅ Provides identity to SAML apps | ✅ Receives identity from SAML IdPs | SAML Guide |
| OAuth2/OIDC | ✅ Provides identity to OAuth2/OIDC apps | ✅ Receives identity from OAuth2/OIDC IdPs | OAuth2/OIDC Guide |
| LDAP/AD | ✅ Authenticates against LDAP/AD, provides identity to apps | ✅ Receives identity from external LDAP/AD | LDAP/AD Guide |
Understanding IDP vs SP
Identity Provider (IdP):
- cidaas provides and provisions user identity to other systems
- Users authenticate with cidaas
- Applications trust cidaas to verify user identity
- Enables Single Sign-On (SSO) across multiple applications
Service Provider (SP):
- cidaas receives user identity from other systems
- Users authenticate with external identity providers
- cidaas trusts external systems to verify user identity
- Enables federated identity and Bring Your Own Identity (BYOI)