Authorization Code Flow
The Authorization Code Flow is one of the OAuth2 flows that was designed to securely authenticate a user and issue an access token. The basic concept behind the authorization code flow is that a code is issued after identification and this must be exchanged for an access token.
This flow requires a client_secret to be securely stored on your backend server. It is recommended for traditional web applications with a secure backend that can protect the client secret from exposure.
How it Works
Before we step into how it works, let's understand some useful parameters.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
client_id | client which represents the business-App in cidaas, where the Resource Owner wants to have access |
redirect_uri | URI where cidaas should redirect to, after login. Must be provided in both authorization request and token exchange request, and must match in both calls |
scope | scope which the user asks for. E.g. profile gives access to profile data |
response_type | type of response. In Authorization Code Flow it has to be code. In cases of the hybrid flow in OIDC it could also be code id-token |
state | random onetime string which will be generated at the beginning of the flow. Recommended to avoid CSRF |
client_secret | suitable client_secret (~ password) for the business-App. Must be kept secure on backend server only |
grant_type | authorization_code needs to be mentioned in code-exchange call to get a token |
code | the one-time-use code must be provided as code parameter |
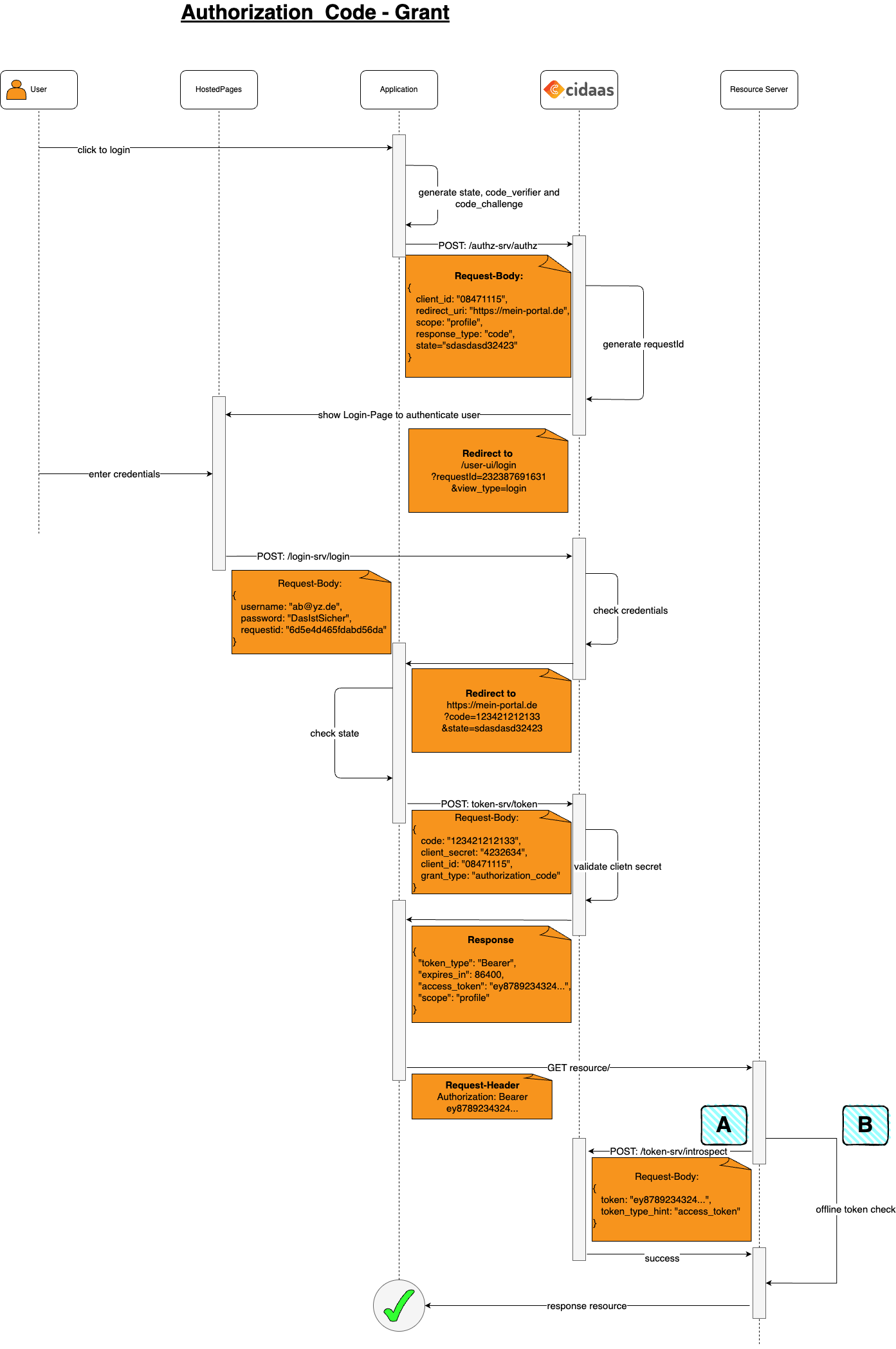
Step 1: The user clicks on login in your application. The login button is nothing less than a authz-srv/authz URL. The Endpoint will verify if the user is already logged in (SSO) and if not will redirect the user to the login page. The authz-endpoint expects multiple parameters: response_type=code, redirect_uri (your redirect URI), client_id (the client_id of your application), scope (requested permissions), and state (a random string for CSRF protection).
Step 2: The user will then enter their credentials on the login page and click on submit. This step involves user authentication, which can be performed using password credentials or passwordless authentication methods such as Magic Link, Email/SMS OTP, or FIDO2.
Step 3: After successful authentication, cidaas will return a code to the provided redirect_uri in the Authz-Call. The client must verify whether the state returned by the authorization server (cidaas) is equal to the state passed in Step 1
Step 4: The Client then requests Access Token from Authorization Server. The backend server makes a secure request to the token endpoint, passing the one-time-use code as code, grant_type=authorization_code, client_id, client_secret, and redirect_uri (must match the redirect_uri from Step 1 for security validation). Upon successful validation, the authorization server returns an access token and optionally a refresh token.
Step 5: The Resource Server validates the Access Token and uses it to serve the requests or retrieve additional details from the /users-srv/userinfo Endpoint.
Security Note
Important: The
client_secretmust be kept secure and stored only on your backend server. Never expose it to client-side code (JavaScript, mobile apps, etc.). If you cannot securely store aclient_secret, use the PKCE Flow instead, which is designed for public clients.
Technical Integration
| API | Description | Link to API |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1: Start Authorization | To perform an authorization request | View API |
| Step 2: Initiate Authentication | To start the user authentication (password or passwordless) | View API |
| Step 3: Perform Authentication | To finish the user authentication | View API |
| Step 4: Continue Login Process | To continue the authentication and receive the authorization code | View API |
| Step 5: Exchange Code | To exchange the code for a token (requires client_secret on backend) | View API |
Example Implementation
Here's an example of how to implement the Authorization Code Flow:
Step 1: Authorization Request
GET https://{{base_url}}/authz-srv/authz?client_id={{client_id}}&redirect_uri={{redirect_uri}}&response_type=code&scope={{scope}}&state={{random_state_string}}
Step 5: Token Exchange (Backend Only)
POST https://{{base_url}}/token-srv/token
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=authorization_code
&client_id={{client_id}}
&client_secret={{client_secret}}
&code={{authorization_code}}
&redirect_uri={{redirect_uri}}
Note: The token exchange must be performed on your backend server where the
client_secretis securely stored. Never perform this request from client-side code.
Need Support?
Please contact us directly on our support page