Groups Role Restriction
Overview
The Group Role Restriction system allows cidaas to control user access during login or SSO by verifying group memberships and roles dynamically. It ensures that users only receive permissions relevant to the consuming application, reducing token payload size.
When a user logs in, cidaas uses the Group Verification API as a Token Condition to check group memberships and roles. The verification results are then embedded as custom claims in the JWT access token, allowing consuming applications to make authorization decisions without additional database lookups.
Key Points:
- The API is primarily used as a Token Condition for group validation during authentication
- The verification results become custom claims in the JWT token (what matters most)
- The API can also be called externally for custom authorization checks if needed
- Only the first relevant group-role match is included in the token to keep it small
Quick Example
Problem: Users belong to multiple groups but each application only needs specific roles
Imagine an organization using cidaas for centralized identity and access management across multiple internal and external applications — like:
| Application | Purpose | Required Roles |
|---|---|---|
| HR Portal | Employee records, leave, payroll | hr-admin, hr-viewer |
| Project Management Tool | Sprint planning, issue tracking | project-manager, developer |
| Customer Support Dashboard | Handling support tickets | support-agent, support-lead |
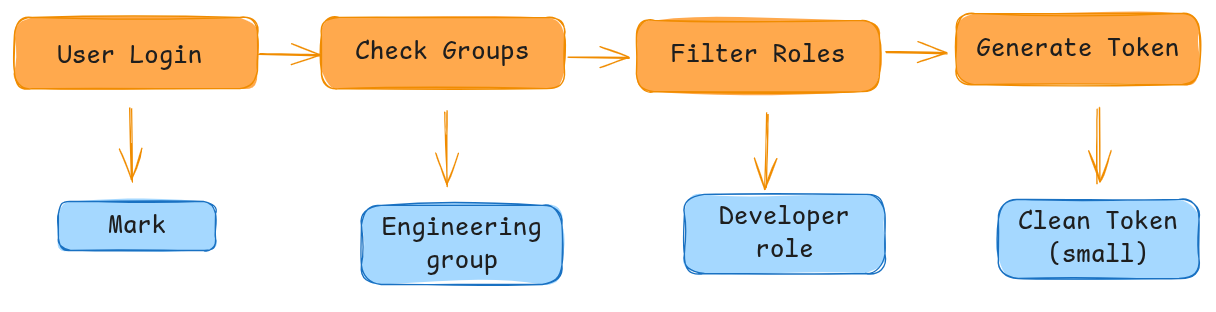
Now, a user named Mark works in the Engineering department. He belongs to the following cidaas Groups and Roles:
| Group Name | Group ID | Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Engineering Team | eng-group | developer, code-reviewer |
| Support Team | support-group | support-agent |
| HR Team | hr-group | hr-viewer |
The Problem:
Without Group Role Restriction, when Mark logs into the HR Portal, his token would contain ALL his roles:
developer,code-reviewer(from Engineering Team) ❌ Not needed for HR Portalsupport-agent(from Support Team) ❌ Not needed for HR Portalhr-viewer(from HR Team) ✅ Only this is needed!
This results in:
- Oversized tokens that can cause "Header Too Large" errors
- Security risk - exposing unnecessary role information
- Confusion - applications see roles they don't need
The Solution:
With Group Role Restriction, when Mark logs into the HR Portal:
- cidaas verifies Mark belongs to
hr-groupwithhr-viewerrole - Only the
hr-viewerrole is added to the token ✅ - Token stays small and secure
- HR Portal only sees relevant permissions
How Verification Works
Benefits
- Enhanced Security: Restricts user access to authorized resources only, preventing unauthorized actions based on group roles
- Optimized Token Size: Includes only relevant roles/groups in authentication tokens, preventing "Header Too Large" errors
- Simplified Permissions: Flattens groups for easier authorization logic and reduced implementation errors
- Seamless Integration: Compatible with Role Based Access Control systems for cross-platform identity management
- No Pre-provisioning Required: Users don't need manual permission setup in target systems
- Real-time Permission Sync: Systems automatically recognize user permissions from JWT tokens upon login
- Audit Trail Tracking: All permission changes and usage are logged for compliance
Core Concepts
Key Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| GVR | Group Verification Request - defines what to check |
| Hint | Controls what data is returned in the response and added to JWT token |
| Filter | Criteria for group/role matching |
| Flattened Roles | Simple list of permissions |
Group Verification Request (GVR)
A GroupVerificationRequest defines the verification logic used to determine if a given user belongs to specific groups and holds required roles. It can be either transient (temporary, for a live check) or persistent (stored for reuse by reference_id).
| Attribute | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | Optional | Unique ID of GVR for persisted requests. You can use an explanatory name since it is used to reference the object. For transient (immediate) verification, omit this field. |
sub | Only if transient | Unique ID of subject. Required for immediate verification calls. For persisted requests, omit this field. |
matchCondition | Yes | Determines whether all (and) or any (or) filters must match |
filters | Yes | Array of group/role criteria to verify |
hints | No | Optional hints controlling what claims are added to the JWT token |
creationTime | Only if persistent | Timestamp (automatically set) |
updatedTime | Only if persistent | Timestamp (automatically set) |
Group Verification Filter
Defines the criteria for selecting user groups to verify membership and role assignment. The Group Verification Filter may contain Role Verification Filters.
Note:
GroupVerificationFiltercan define either a specific User Group (groupId) or a User Group Type (groupType) to filter multiple groups of the same type.
| Attribute | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
groupId | No | Optional group ID to filter by specific group |
groupType | No | Optional group type to filter multiple groups of the same type |
roleFilter | No | Optional role filter to check specific roles within the group(s) |
Role Verification Filter
| Attribute | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
matchCondition | Yes | Logical condition for matching roles |
roles | Yes | Roles required for verification |
Match Conditions
The verification system supports two match conditions between filters:
"and"(AndCondition) - User must satisfy ALL filters"or"(OrCondition) - User must satisfy ANY filter
OR Condition ("or")
- Behavior: Returns immediately when any filter matches.
- Groups Added: Only groups from the first matching filter.
- Roles Added: Only roles from the first matching filter.
Example:
{
"sub": "user123",
"matchCondition": "or",
"filters": [
{"groupId": "eng-group", "roleFilter": {"roles": ["developer"]}},
{"groupId": "user-group", "roleFilter": {"roles": ["user"]}},
{"groupType": "project", "roleFilter": {"roles": ["project-manager"]}}
],
"hints": ["groupIds", "rolesOfGroup", "allowedGroups"]
}
If user is in eng-group with developer role:
- Result:
verified: true. - Token Claims Added:
groupIds:["eng-group"]rolesOfGroup:["developer"]allowedGroups:[{"groupId": "eng-group", "roles": ["developer"]}]
- Processing: Stops after first match (OR condition).
AND Condition ("and")
- Behavior: Must satisfy ALL filters, but processes each filter separately.
- Groups Added: Groups from ALL matching filters.
- Roles Added: Roles from ALL matching filters (deduplicated).
Example:
{
"sub": "user123",
"matchCondition": "and",
"filters": [
{"groupId": "eng-group", "roleFilter": {"roles": ["project-manager"]}},
{"groupType": "project", "roleFilter": {"roles": ["developer"]}}
],
"hints": ["groupIds", "rolesOfGroup", "allowedGroups"]
}
If user is in eng-group AND in a project group:
- Result:
verified: true. - Token Claims Added:
groupIds: ["eng-group", "project-group"]rolesOfGroup: ["project-manager", "developer"]allowedGroups:[
{"groupId": "eng-group", "roles": ["project-manager"]},
{"groupId": "project-group", "roles": ["developer"]}
]
- Processing: Includes data from all matching filters (AND condition).
Token Claims
Important: While the API returns a response, the crucial part is what gets added as custom claims to the JWT access token. These claims are what consuming applications use for authorization decisions.
The verification system supports the following valid hint values that control what additional data is added as custom claims to the JWT token:
Note: Each hint adds specific claims to the token. You can use multiple hints to add different claim types.
Group Verification Hints
GVRHint defines what additional data will be returned post-verification and also what might be added as custom claims in the ID or access token.
| Hint Value | Description |
|---|---|
default | Returns only verified status |
groupIds | Returns all matching group IDs |
rolesOfGroup | Returns deduplicated list of roles from matched group(s) |
allowedGroups | Returns full group-role mapping per group |
Hint: "default" (GVRHintDefault)
- Purpose: Minimal token claim - only verification status.
- Token Claim: No additional claims added (verification happens but no claims in token)
- Use Case: When you only need to know if access is granted during login, but don't need role information in the token.
- Note: While the API response includes
verified: true/false, this hint doesn't add claims to the token. Use other hints if you need role/group information in the token.
Hint: "groupIds" (GVRHintGroupIDsArray)
- Purpose: Adds group IDs that matched the verification criteria to the JWT token.
- Token Claim: Adds
groupIdsarray to the JWT token claims. - Use Case: When your application needs to know which specific groups the user belongs to for authorization decisions.
JWT Token Claim (what gets added to the token):
{
"groupIds": ["eng-group"]
}
Hint: "rolesOfGroup" (GVRHintRolesOfGroup)
- Purpose: Adds all unique roles the user has across all matched groups to the JWT token.
- Token Claim: Adds
rolesOfGrouparray to the JWT token claims. - Use Case: When your application needs a flattened list of roles for authorization decisions. This is the most commonly used hint.
JWT Token Claim (what gets added to the token):
{
"rolesOfGroup": ["developer", "project-manager"]
}
Hint: "allowedGroups" (GVRHintAllowedGroups)
- Purpose: Adds detailed group-role mappings for each matched group to the JWT token.
- Token Claim: Adds
allowedGroupsarray to the JWT token claims. - Use Case: When your application needs the most detailed information about user's group memberships with their associated roles.
JWT Token Claim (what gets added to the token):
{
"allowedGroups": [
{
"groupId": "eng-group",
"roles": ["developer", "project-manager"]
}
]
}
Using Multiple Hints
You can use multiple hints together to add different claim types to the JWT token.
Example Request (used as Token Condition during authentication):
POST /groups-srv/verifications
{
"sub": "user123",
"matchCondition": "or",
"filters": [
{
"groupId": "eng-group",
"roleFilter": {
"roles": ["developer", "project-manager"],
"matchCondition": "or"
}
}
],
"hints": ["groupIds", "rolesOfGroup", "allowedGroups"]
}
JWT Token Claims (what gets added to the token - this is what matters):
{
"groupIds": ["eng-group"],
"rolesOfGroup": ["developer", "project-manager"],
"allowedGroups": [
{
"groupId": "eng-group",
"roles": ["developer", "project-manager"]
}
]
}
How It Works
Primary Use: Token Condition
Related: Learn more about Token Conditions and Prechecks to understand how this fits into the authentication flow.
The Group Verification API is primarily used as a Token Condition during the authentication flow. When a user authenticates:
- cidaas automatically calls the verification API as part of token condition processing
- The verification results are embedded as custom claims in the JWT access token
- The consuming application receives the token with the claims already populated
- No additional API calls needed by the application
Secondary Use: External Custom Checks
The API can also be called externally by your applications for custom authorization checks:
- Pre-flight authorization checks before API calls
- Custom permission validation logic
Endpoint: POST /groups-srv/verifications
- Purpose: Validates user group membership and roles
- Primary Use: Token Condition = group validation during authentication
- Secondary Use: Can be called externally for custom checks
- Authentication: Bearer token required
Authorization Access
The Group Verification API provides a mechanism to check individual user access permissions in real-time. This enables applications to:
- Verify Access Before Operations: Check if a user has the required group memberships and roles before allowing access to protected resources
- Dynamic Permission Validation: Perform authorization checks without relying solely on JWT token claims
- Real-time Access Control: Validate permissions at the point of access, ensuring up-to-date authorization decisions
- Custom Authorization Logic: Implement application-specific authorization rules by calling the verification API directly
Authentication Requirements:
- The endpoint requires authentication via Bearer token
- For anonymous tokens, the
cidaas:users_readscope is required - Non-admin users can only verify their own access unless they have admin roles
- Admin users can verify access for any user
Use Cases for Individual Access Checks:
- API Gateway Authorization: Verify user permissions before routing requests to backend services
- Resource-Level Access Control: Check if a user can access specific resources based on group memberships
- Dynamic Permission Updates: Verify permissions when group memberships change, without requiring re-authentication
- Audit and Compliance: Log authorization decisions by verifying access at the point of resource access
Real World Usage Scenarios
Scenario 1: Multi-Tenant SaaS Application
Challenge: A SaaS platform serves multiple customers (tenants). Each customer's users should only see their own tenant's data.
Solution: Create a Group Verification Request per tenant:
- Tenant A users: Verify
groupId: "tenant-a"with roletenant-member - Tenant B users: Verify
groupId: "tenant-b"with roletenant-member
Result: When users log in, their token only contains their tenant group ID. The application can immediately route them to the correct tenant data without additional database queries.
Scenario 2: Enterprise Application Suite
Challenge: Large enterprise has 20+ applications. Users belong to multiple departments but each app should only see relevant roles.
Solution: Configure Group Verification Request per application:
- Finance App: Only verify
finance-departmentgroups - Engineering App: Only verify
engineering-departmentgroups - HR App: Only verify
hr-departmentgroups
Result: Users get application-specific tokens with only relevant roles, preventing role confusion and keeping tokens small.
Scenario 3: Compliance and Audit Requirements
Challenge: Need to ensure users only access resources they're authorized for, with full audit trail.
Solution: Group Verification ensures:
- Only verified group memberships appear in tokens
- All verification attempts are logged
- Failed verifications block access automatically
Result: Complete audit trail of who accessed what, when, and why access was granted or denied.
Flattened Role Lists
A Flattened Role List means that all the user's permissions are listed in a simple, flat structure — no hierarchies, no nested groups, and no role chaining. It's the easiest form of role representation where each role is just a plain entry in a list or array.
Why Flattened Role Lists
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
- Performance: Fast permission checks.
- Flexibility: Easy to add/remove permissions.
- Debugging: Clear what permissions a user has.
- Caching: Easy to cache permission lists.
- Microservices: No need for complex group hierarchies.
Use Case: Open Policy Agent (OPA)
How it works:
- Uses Rego policies with flat permission lists
- No hierarchical structure - just boolean permission checks
- Perfect for JWT role mapping
# OPA Policy using flattened roles
package auth
import input.jwt.claims
# Map JWT roles to permissions
permissions := {
"admin": ["users:read", "users:write", "users:delete", "projects:manage"],
"developer": ["projects:read", "projects:write", "code:commit"],
"user": ["profile:read", "profile:write"]
}
# Check if user has permission
allow {
user_roles := claims.rolesOfGroup
required_permission := input.permission
user_permissions := {p | role := user_roles[_]; p := permissions[role]}
required_permission in user_permissions
}
Integration Examples
For detailed integration examples with Spring Security, Django REST Framework, Apache Shiro, Open Policy Agent (OPA), and other frameworks, see Group Role Restrictions - Integration Examples.
The integration guide includes:
- Complete code examples for each framework
- How to extract and use JWT token claims (
rolesOfGroup,groupIds,allowedGroups) - Best practices for permission mapping
- Common integration patterns
Technical Integration
The following APIs are available for managing group verification requests and performing authorization checks:
Authorization and Access Verification
| API | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Check User Group Restrictions | Verify individual user access permissions by checking group memberships and roles. Use this API for real-time authorization checks, pre-flight permission validation, or custom authorization logic. | View API |
Group Verification Request Management
| API | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Get All Group Verification Requests | Retrieve all group verification requests using graph filter | View API |
| Create Group Verification Request | Create a new persistent group verification request that can be reused by reference ID | View API |
| Get Group Verification Request by ID | Retrieve a specific group verification request by its unique ID | View API |
| Update Group Verification Request by ID | Update an existing group verification request | View API |
| Delete Group Verification Request by ID | Delete a group verification request | View API |
| Verify User Group Restrictions by Request ID | Verify user access using a stored verification request ID and user sub (GET method) | View API |
Summary
This entire setup is a smart permission check during login. It makes sure:
- Your roles and groups are checked against what the app expects.
- Your token stays small and precise.
- Only the needed permissions go into your access card (token).
Need Support?
Please contact us directly on our support page.